Kampala, Uganda – The Uganda Bureau of Statistics (UBOS) released the final findings from the National Population and Housing Census 2024, shedding light on the state of housing infrastructure across the country.
The data reveals a mixed picture, with significant progress in some areas but persistent challenges in others.
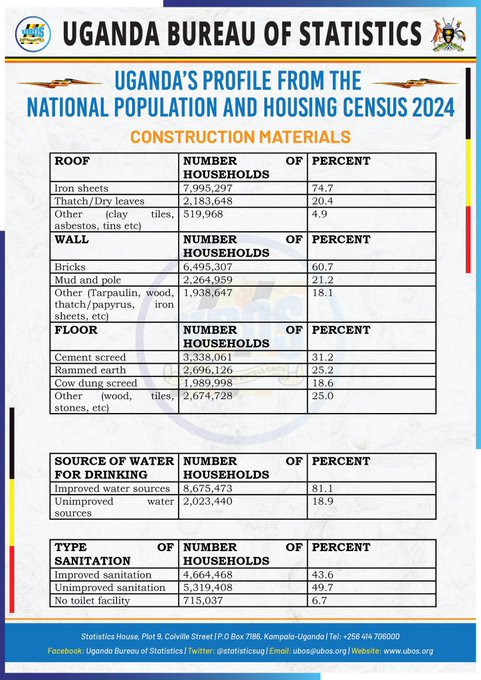
Roofing
Iron sheets have emerged as the dominant roofing material, covering 74.7% of households. This indicates a shift away from traditional materials like thatch and dry leaves.
Walls
Bricks are the most common wall construction material, used in 60.7% of households. Mud and pole structures are still prevalent, accounting for 21.2% of households.
Floors
Cement screed has become the preferred flooring material, used in 31.2% of households. Rammed earth and cow dung screed remain common, particularly in rural areas.
Water and Sanitation
Access to improved water sources has increased significantly, with 81.1% of households having access. However, sanitation remains a challenge, with only 43.6% of households having access to improved sanitation facilities.
Analysis and Implications:
The data highlights the ongoing urbanisation and modernisation of Uganda, with a clear shift towards more durable and modern building materials. However, significant disparities remain in access to basic amenities like clean water and sanitation.
The government and stakeholders can leverage these insights to promote sustainable construction. Encouraging the use of eco-friendly and locally sourced materials can reduce environmental impact and promote sustainable building practices.
It can also use this data to improve access to water and sanitation. Expanding access to clean water and sanitation facilities is crucial for improving public health and reducing disease.
With this data, the government can address housing disparities. Policies and programmes aimed at improving access to affordable housing, particularly for low-income households, are necessary to ensure equitable access to decent living conditions.
The census data provides a valuable snapshot of housing conditions in Uganda. By understanding the challenges and opportunities, policymakers and stakeholders can develop effective strategies to improve housing infrastructure and enhance the quality of life for all Ugandans.











